Analysing the Min-Cut Contiguous Path
Brick Example
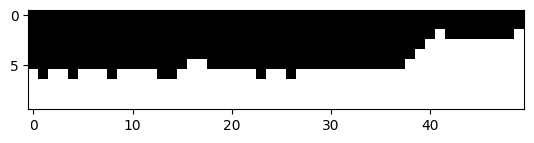
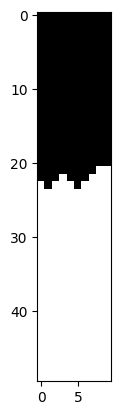
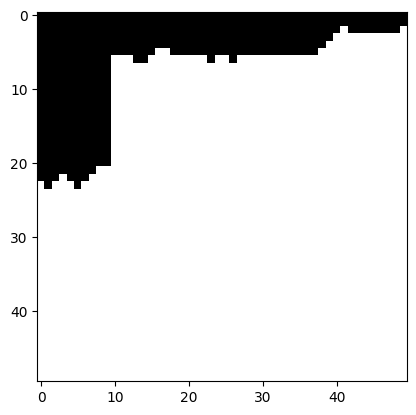
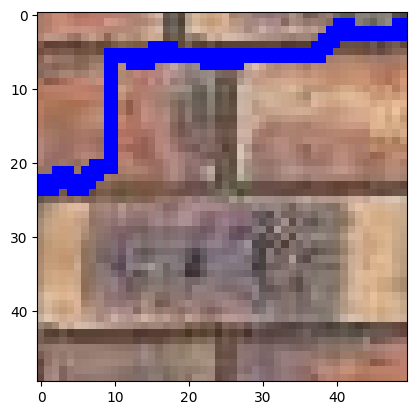
In the case of bricks_small.jpg, the Sum of Squared Differences (SSD) map reveals that the lowest SSD cost occurs
along the lines between the bricks, which correspond to noticeable edges in the image. Consequently, the min-cut
path predominantly follows these dominant edges, i.e., the lines separating the bricks.
Interestingly, the path remains consistent along these edges until it transitions to another edge above. This transition occurs in a region where the pixel values change gradually, ensuring a seamless overlap. Specifically, the path cuts through areas with evenly red-colored portions of the brick to maintain the visual consistency of the overlap.


quilt_cut


Text Example
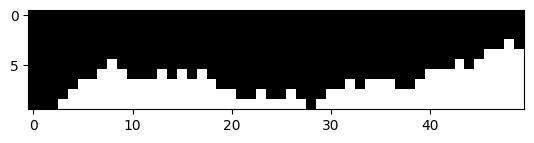
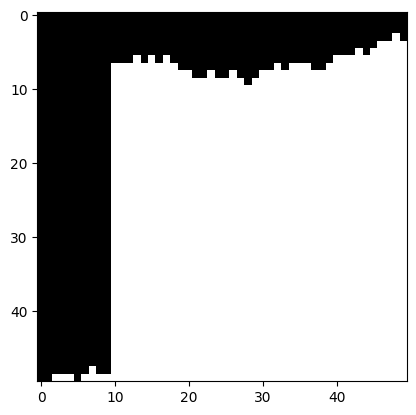
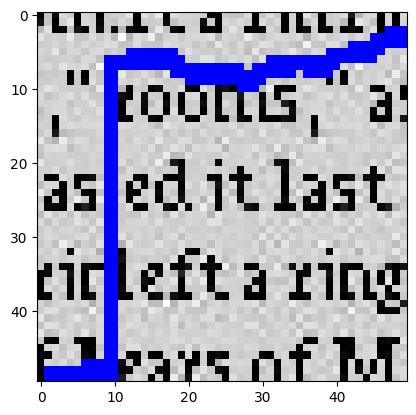
For text.jpg, the SSD map highlights that the ssd_cost is lowest where the text is located.
As a result, the min-cut path aligns itself along a line of text, which serves as the dominant edge.
However, when the path encounters vertical white spaces—caused by word spacing or text alignment in real life—it strategically
passes through these wider gaps. This approach guarantees low ssd_cost and ensures smooth transitions
in the overlapping areas.


quilt_cut